What is an enterprise switch and how does it differ from a consumer switch?
An enterprise switch is a high-performance networking device designed for larger organizations, providing the connectivity, reliability, and scalability needed for complex IT infrastructures. Unlike consumer switches, which are typically used in home or small office networks, enterprise switches support features like VLANs, quality of service (QoS), advanced security measures, and high throughput, which are critical for managing large-scale networks.
What are the main types of enterprise switches?
There are three main types of enterprise switches: managed, unmanaged, and smart switches. Managed switches offer full control over network traffic and advanced configuration options, including VLANs, monitoring, and security features. Unmanaged switches are plug-and-play devices with no configuration options, ideal for smaller, less complex environments. Smart switches are a middle ground, providing basic management features like VLAN support but with fewer options than fully managed switches.
Why is VLAN support important in enterprise switches?
VLAN (Virtual Local Area Network) support allows network administrators to segment network traffic logically without physical separation. This improves network efficiency, enhances security by isolating different departments, and reduces broadcast traffic. VLAN support is essential in enterprise environments for managing large networks and maintaining high performance and security standards.
How does QoS (Quality of Service) function in an enterprise switch?
QoS in enterprise switches is a feature that prioritizes traffic, ensuring that critical applications like VoIP, video conferencing, and real-time data receive higher priority over less time-sensitive traffic such as email or file transfers. This reduces latency and packet loss, improving network performance for high-priority applications.
What are the key security features in enterprise switches?
Enterprise switches incorporate various security features, including port security, access control lists (ACLs), 802.1X network access control, and MAC address filtering. These features help prevent unauthorized devices from connecting to the network, ensure that only authenticated users can access certain network resources, and protect against potential security breaches.
What is Power over Ethernet (PoE) in enterprise switches?
Power over Ethernet (PoE) is a technology that allows enterprise switches to deliver both data and power over a single Ethernet cable. This is particularly useful for powering devices like IP phones, wireless access points, and security cameras without the need for separate power supplies, making network installations cleaner and more cost-effective.
What is the role of Layer 3 switching in an enterprise network?
Layer 3 switches combine the functions of traditional Layer 2 switches with routing capabilities. These switches can route traffic between different subnets or VLANs, improving network efficiency and reducing the need for a separate router in many cases. Layer 3 switching is essential for large-scale enterprise networks that require advanced traffic management.
How do stackable switches benefit enterprise networks?
Stackable switches allow multiple physical switches to be connected together and function as a single logical unit. This provides greater scalability and redundancy, as well as simplified management. Stackable switches are ideal for growing enterprise networks, allowing easy expansion without the need to reconfigure or replace hardware.
What are some common challenges in managing enterprise switches?
Common challenges include ensuring network security, managing traffic bottlenecks, maintaining high availability, and properly configuring VLANs and QoS settings. Additionally, monitoring and diagnosing network performance issues can become complex as enterprise networks grow, requiring sophisticated tools and expertise.
How do enterprise switches support network scalability?
Enterprise switches support scalability through features like stacking, modular design, and high port density. These features allow network administrators to add more switches or ports to accommodate growing network traffic without disrupting the existing infrastructure. This makes it easier for enterprises to scale their networks as business demands increase.
What is the difference between Layer 2 and Layer 3 switches?
Layer 2 switches operate at the data link layer and are responsible for switching data frames based on MAC addresses within the same network segment. They cannot route traffic between different subnets. Layer 3 switches, on the other hand, combine Layer 2 switching functions with routing capabilities, enabling them to route traffic between different subnets or VLANs.
What are some use cases for using a managed enterprise switch?
Managed switches are ideal for enterprise environments that require advanced network management, security, and scalability. Use cases include large corporate offices, data centers, or campuses where network segmentation, high security, and traffic management are required. Managed switches allow for remote monitoring and configuration, making them suitable for environments where uptime and performance are critical.
How do enterprise switches improve network performance?
Enterprise switches improve network performance by providing higher bandwidth, reducing latency, and optimizing traffic flow. Features like QoS, link aggregation, and Layer 3 routing ensure that critical data is prioritized and that network resources are allocated efficiently, leading to better overall network performance.
Can enterprise switches be used in a data center environment?
Yes, enterprise switches are essential in data centers due to their high-performance capabilities, reliability, and scalability. They handle large volumes of data traffic, support advanced routing and switching features, and provide high levels of redundancy and fault tolerance, making them a critical part of any data center infrastructure.
What role does redundancy play in enterprise switches?
Redundancy in enterprise switches is essential for ensuring high availability and preventing network downtime. Features like link aggregation, stackable switches, and dual power supplies ensure that if one component fails, another can take over without interrupting network operations, providing fault tolerance for critical applications.
How do enterprise switches integrate with other network devices?
Enterprise switches integrate with routers, firewalls, servers, and wireless access points through standard networking protocols such as Ethernet, IP, and VLANs. They also support network management protocols like SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol) for remote monitoring and configuration, allowing seamless communication with other network devices in a complex infrastructure.
What are some of the most popular brands of enterprise switches?
Some of the most popular brands for enterprise switches include Cisco, Juniper, Arista, HPE (Aruba), and Dell. These companies provide a wide range of enterprise-grade switches that support high throughput, advanced features, and scalability, making them top choices for businesses across various industries.
What is the role of SNMP in managing enterprise switches?
SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol) is used to monitor and manage network devices, including enterprise switches. It allows network administrators to gather performance data, configure devices, and receive alerts about potential issues. SNMP helps ensure the smooth operation of the network by providing real-time insights into switch performance and health.
What is the difference between a switch and a hub in an enterprise network?
A switch operates at the data link layer (Layer 2) and can intelligently forward data to the specific device on the network based on MAC addresses, reducing network congestion. A hub, on the other hand, broadcasts data to all connected devices, leading to unnecessary traffic and reduced efficiency. In enterprise networks, switches are preferred due to their superior performance and security features.
What is the importance of port density in enterprise switches?
Port density refers to the number of network ports available on a switch. High port density in enterprise switches allows for greater scalability and flexibility, enabling businesses to connect multiple devices without needing additional switches. This is crucial in environments with a large number of users or devices that require constant connectivity.
What is a Layer 3 switch’s routing capability?
A Layer 3 switch’s routing capability enables it to route data packets between different IP subnets, similar to a traditional router. This function reduces network bottlenecks by eliminating the need for separate routers in certain configurations, making Layer 3 switches ideal for medium-to-large enterprise networks that need both switching and routing functionalities.
Can enterprise switches handle high traffic volumes?
Yes, enterprise switches are designed to handle high traffic volumes. They feature high bandwidth, multiple ports, and advanced traffic management capabilities like link aggregation, which enables them to manage large amounts of data without compromising performance. These switches are essential for environments like data centers and large enterprises with heavy network traffic.
How do enterprise switches support network virtualization?
Enterprise switches support network virtualization by enabling features like VLANs, VXLAN (Virtual Extensible LAN), and software-defined networking (SDN). These technologies allow the creation of virtual networks on top of a physical infrastructure, providing more flexibility, efficient use of resources, and improved network management in a virtualized environment.
What are the advantages of using a 10GbE (10 Gigabit Ethernet) enterprise switch?
A 10GbE switch provides significantly higher data transfer speeds compared to standard 1GbE switches, making it ideal for bandwidth-intensive applications such as data center operations, cloud services, and large-scale enterprise networks. It supports faster communication, reduces latency, and can handle larger volumes of traffic, ensuring high performance in demanding environments.
How do enterprise switches help with network monitoring and diagnostics?
Enterprise switches often come with built-in network monitoring features such as SNMP support, traffic analysis tools, and port mirroring. These tools allow administrators to track network performance, detect anomalies, and identify potential issues. Proactive monitoring helps prevent downtime and ensures optimal network performance.
What is link aggregation in enterprise switches?
Link aggregation is a technique that combines multiple physical network links into a single logical connection. This improves bandwidth, enhances redundancy, and provides load balancing. Enterprise switches support link aggregation protocols like LACP (Link Aggregation Control Protocol), which ensures efficient traffic distribution across multiple links while providing higher fault tolerance.
What is the role of Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) in enterprise switches?
Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) is used in enterprise switches to prevent network loops by creating a loop-free topology. STP dynamically disables redundant paths in the network while ensuring that a backup path becomes active if the primary one fails. This helps maintain network stability and prevents broadcast storms in larger enterprise networks.
How do enterprise switches support multicast traffic?
Enterprise switches support multicast traffic through protocols like IGMP (Internet Group Management Protocol) and PIM (Protocol Independent Multicast). These protocols enable efficient delivery of multicast data streams, such as video conferencing or IPTV, to multiple recipients without flooding the entire network with unnecessary traffic.
Can enterprise switches support IPv6?
Yes, most modern enterprise switches support IPv6, the next-generation internet protocol. IPv6 support is essential as organizations move toward a more scalable, secure, and efficient network addressing system. Enterprise switches with IPv6 support ensure compatibility with newer devices and networks, preparing businesses for the future of networking.
How do enterprise switches ensure high availability and fault tolerance?
Enterprise switches ensure high availability and fault tolerance through features like redundant power supplies, stacking capabilities, and automatic failover mechanisms. By utilizing technologies like link aggregation and Spanning Tree Protocol, switches can automatically reroute traffic in the event of a failure, ensuring minimal disruption to network services.
What is the role of a PoE+ (Power over Ethernet Plus) switch in an enterprise environment?
PoE+ switches deliver both data and power over Ethernet cables, providing up to 25.5 watts of power per port. This higher power output is crucial for powering more demanding devices like high-performance IP cameras, telephones, and wireless access points. PoE+ simplifies installations by eliminating the need for separate power cables for these devices.
What is the significance of network segmentation in enterprise switches?
Network segmentation using VLANs is crucial in enterprise environments to isolate traffic, improve performance, and enhance security. By dividing the network into smaller, manageable segments, enterprises can prevent broadcast storms, minimize congestion, and secure sensitive data by restricting access to certain groups or departments.
How do enterprise switches support software-defined networking (SDN)?
Enterprise switches are key components in SDN architectures, where they can be centrally managed and programmed through software. SDN provides greater flexibility by decoupling the control plane from the data plane, enabling dynamic and real-time network configuration changes. This is essential for businesses seeking to optimize and automate their network operations.
How do enterprise switches ensure efficient handling of broadcast traffic?
Enterprise switches use VLANs to reduce broadcast traffic by segmenting the network. By dividing the network into smaller segments, switches ensure that broadcast traffic is contained within those segments, minimizing the impact on overall network performance. Additionally, protocols like IGMP snooping can help manage multicast traffic and optimize network efficiency.
What is the role of a core switch in an enterprise network?
A core switch is a high-performance, high-capacity switch positioned at the core of an enterprise network. It connects multiple distribution and access layer switches and serves as the backbone of the network, ensuring fast data transmission between different segments of the network. Core switches typically support high-speed interfaces and advanced routing capabilities.
How do enterprise switches handle security attacks like DoS (Denial of Service)?
Enterprise switches protect against DoS attacks through a variety of mechanisms, including rate-limiting, access control lists (ACLs), and traffic filtering. They can identify abnormal traffic patterns and block malicious traffic before it overwhelms the network. Advanced security features like port security and 802.1X authentication also help prevent unauthorized access, reducing the risk of attacks.
What is the difference between a stackable and non-stackable enterprise switch?
Stackable switches can be physically linked together to form a single logical unit, making it easier to expand network capacity without additional configuration. Non-stackable switches, on the other hand, operate independently, and additional switches need to be individually managed and configured. Stackable switches are preferred for larger networks that require scalability and simplified management.
What are the benefits of 40GbE and 100GbE enterprise switches?
40GbE and 100GbE enterprise switches offer ultra-high-speed data transfer, essential for modern data centers and high-performance applications like cloud computing and big data analytics. These switches reduce latency, increase throughput, and allow for efficient handling of large volumes of data, ensuring optimal performance in demanding network environments.
How do enterprise switches handle traffic prioritization for real-time applications?
Enterprise switches prioritize real-time applications like VoIP and video conferencing using QoS (Quality of Service) settings. By classifying and marking traffic based on its priority, switches can ensure that time-sensitive traffic is processed first, minimizing delays and ensuring high-quality user experiences for critical applications.
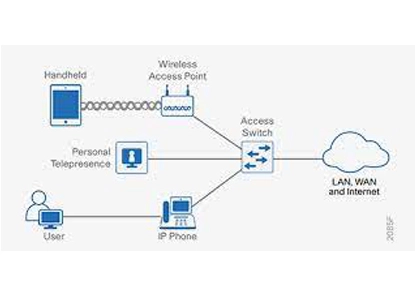
What is the role of an access layer switch in an enterprise network?
An access layer switch connects end-user devices like computers, phones, and printers to the network. It serves as the entry point to the network, providing port-level security and enabling the implementation of policies like QoS and VLANs. Access layer switches are often connected to distribution layer switches, which aggregate traffic and provide higher-level routing and control.
How do enterprise switches support network automation?
Enterprise switches support network automation through protocols like NETCONF, REST APIs, and software integration tools. These features enable automated network provisioning, configuration management, and real-time monitoring. Automation helps streamline operations, reduce errors, and improve network agility, which is crucial for modern enterprises that require flexibility and efficiency.
How can enterprises ensure network security with enterprise switches?
Enterprise switches offer several security features to protect the network, including 802.1X authentication, MAC address filtering, port security, and access control lists (ACLs). These features restrict unauthorized access to the network, ensuring that only legitimate devices and users can connect. Additionally, monitoring and logging features allow administrators to track and respond to potential security threats.
Can enterprise switches support network redundancy protocols like HSRP or VRRP?
Yes, enterprise switches support redundancy protocols like HSRP (Hot Standby Router Protocol) and VRRP (Virtual Router Redundancy Protocol), which ensure high availability by providing backup routes in case of a failure. These protocols help maintain network uptime by automatically rerouting traffic to a backup router or switch if the primary device goes down.
How do enterprise switches handle large amounts of multicast traffic?
Enterprise switches handle multicast traffic using protocols like IGMP snooping, which ensures that multicast data is only forwarded to the appropriate devices on the network. This reduces unnecessary load on devices that do not need the multicast stream and improves network efficiency, especially in environments with high levels of multimedia content like video streaming.
What are the benefits of using a modular enterprise switch?
Modular enterprise switches allow for greater flexibility and scalability, as they can be equipped with different modules to suit the specific needs of the network. These switches can be easily upgraded or expanded by adding new modules for additional ports, power supplies, or even advanced features like security or routing capabilities, making them ideal for evolving enterprise networks.
How can enterprise switches optimize cloud connectivity?
Enterprise switches optimize cloud connectivity by supporting high-bandwidth connections, Quality of Service (QoS), and cloud-aware routing protocols. They enable seamless communication between on-premise data centers and cloud environments, ensuring low-latency access to cloud applications and services. Many switches also support SD-WAN (Software-Defined Wide Area Networking), which enhances cloud application performance.
How do enterprise switches facilitate network virtualization and multi-tenant environments?
Enterprise switches support network virtualization by allowing the creation of multiple virtual networks (VLANs or VXLANs) on the same physical switch. This is crucial for multi-tenant environments, where different organizations or departments can share the same infrastructure while maintaining logical separation for security and performance reasons.
What is the importance of network analytics in enterprise switches?
Network analytics in enterprise switches help administrators monitor traffic patterns, detect anomalies, and identify performance bottlenecks in real time. By using analytics tools built into the switches, network operators can proactively address issues, optimize resource allocation, and ensure that the network meets the growing demands of the business.
How do enterprise switches enable high-performance computing (HPC) environments?
Enterprise switches are crucial in HPC environments, where large-scale computing clusters require fast and reliable network connectivity. By supporting high-speed interfaces like 10GbE, 40GbE, and 100GbE, and features like low-latency switching, these switches facilitate the rapid transfer of data between nodes, ensuring that compute-intensive workloads are handled efficiently.
What are the key considerations when selecting an enterprise switch?
When selecting an enterprise switch, key considerations include port density, scalability, supported protocols, security features, power efficiency, and support for high-speed networking standards like 10GbE or 100GbE. Additionally, businesses should consider the switch's ability to integrate with existing infrastructure, ease of management, and vendor support options.
 Internet Data Center
Internet Data Center FAQs
FAQs Industry News
Industry News About Us
About Us Data Center Switch
Data Center Switch  Enterprise Switch
Enterprise Switch  Industrial Switch
Industrial Switch  Access Switch
Access Switch  Integrated Network
Integrated Network  Optical Module & Cable
Optical Module & Cable 
























 Call us on:
Call us on:  Email Us:
Email Us:  2106B, #3D, Cloud Park Phase 1, Bantian, Longgang, Shenzhen, 518129, P.R.C.
2106B, #3D, Cloud Park Phase 1, Bantian, Longgang, Shenzhen, 518129, P.R.C.