In the world of enterprise networking solutions, understanding the technology behind efficient data transmission is crucial. One such technology that plays a pivotal role is the Direct Attach Cable (DAC cable). Direct attach cables are becoming increasingly integral for networks striving for high performance and cost efficiency. This article explores what direct attach cables are, how they function, their benefits over fiber alternatives, their length and speed limitations, and their typical deployment scenarios within the networking landscape. Whether you're dealing with data center setups or industrial switch arrays, grasping the nuances of DAC cables can enhance your engineering toolkit.
What are DAC Cables?
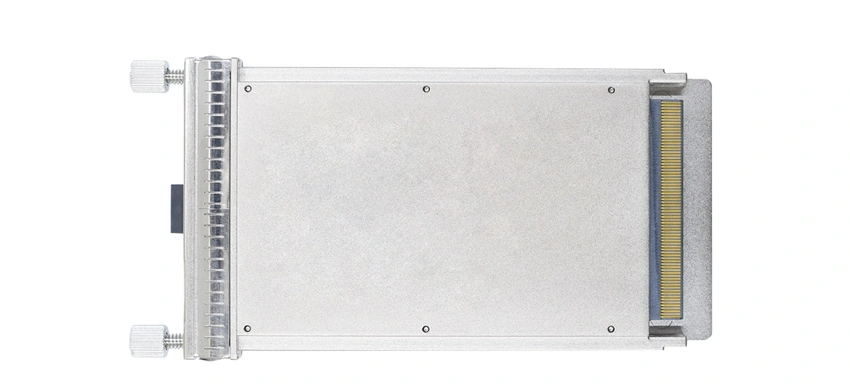
Direct Attach Cables (DAC cables) are a type of high-speed cable used to connect networking equipment, such as routers and switches, within a network setup. Unlike fiber optic cables, direct attach cables consist of twinax copper wiring and terminate with optical transceiver modules, typically at each end. These cables are frequently seen in rackmount network switch situations due to their plug-and-play nature and streamlined installation process.
Parameter | Copper (DAC Cable) | Fiber Optic |
Material | Copper | Glass |
Cost | Lower | Higher |
Range | Short | Long |
Flexibility | Higher | Lower |
DAC cables offer a reliable solution for short distances, often used to connect devices within the same rack or across adjacent racks. They are available in multiple options like SFP DAC, 10G SFP modules, and more based on the specific networking requirements.

How DAC Cables Function
The functioning of a direct attach cable starts with its construction. It combines twisted pair copper cabling with robust connectors, ensuring durability and efficient data transmission. The connectors frequently integrate optical transceiver modules, enhancing their functionality by converting electrical signals into optical ones and vice versa. These modules play an integral part in ensuring low latency and high-speed data transfer across network switch layers.
Unlike layer 2 switches which typically operate on a simpler scale, DAC cables ensure that layer 3 network switch operations—handling routing tasks—are optimized. As an SFP transceiver module, it minimizes signal interference, crucial for unmanaged Ethernet switch environments where network traffic can be less predictable.
Benefits Over Fiber Alternatives
Comparing DAC cables to fiber alternatives, several advantages become evident. Primarily, DAC cables are celebrated for their cost-efficiency. Due to their simpler production process and materials, DAC cables are typically less expensive than equivalent fiber setups. This can be advantageous in contexts where budget constraints are a significant consideration.
Cost Efficiency: Compared to optical AOC cables or active optical cables, direct attach cables are cheaper, offering similar performance for short-reach applications.
Simplicity: Plug-and-play capability ensures easy installation and maintenance without the need for additional tools or intricate adjustments.
Interference Resistance: The copper design is less susceptible to interference from electromagnetic fields, which can be crucial in industrial LAN switch environments.
These benefits make DAC cables a leading choice particularly in access switch scenarios where reliable performance is non-negotiable.
Length and Speed Limitations
Despite their advantages, direct attach cables do have specific limitations. The primary constraints of DAC cables concern length and speed capabilities, which differ substantially from fiber options.
Length Restrictions: Typically, DAC cables are designed for handling distances up to 7 meters, making them ideal for rack mount Ethernet switch setups but less suitable for long-distance operations.
Speed Performance: While direct attach cables boast impressive speeds for short distances, usually supporting up to 10Gbps, they fall short when compared to long-haul fiber options.
These limitations necessitate a strategic approach in choosing between DAC or fiber optic patch cord solutions based on the specific Ethernet switch rack configuration and network demands.

Typical Deployment Scenarios
In practical deployment, DAC cables are preferred in scenarios requiring high port density and efficiency. Their applicability spans several areas:
Data Centers: Within rack mount switch environments, direct attach cables efficiently interconnect devices while maintaining robust signal integrity.
Industrial Applications: Often utilized in industrial managed switch and industrial Ethernet switch setups due to their durability and flexibility.
Edge Computing: In IoT edge gateway applications, DAC cables ensure seamless data flow between devices under ever-expanding smart pole networks, providing a backbone for outdoor network switch configurations.
Their role in these scenarios underscores why professionals in networking continually leverage DAC cables to streamline their infrastructural workflows.
Conclusion
The direct attach cable stands out as a versatile, cost-effective choice within networking infrastructure, especially where short-distance, high-speed connectivity is required. As networks continue to evolve towards more dynamic configurations like Ethernet media converter enhanced setups, understanding and utilizing DAC cables ensure your infrastructure remains competitive. Future trends may see even more integration of direct attach cables in new technologies, making it an indispensable tool for both specialists in layer two switch technology and broader network architects. Whether planning for enhancements in industrial routers or optimizing L3 network switch arrays, direct attach cables remain a cornerstone in the ever-expanding realm of enterprise networking solutions.
By Jennifer Tseng
Hi, I'm Jennifer, Marketing Executive at lanaotek.com.
I specialize in translating cutting-edge optical and Ethernet transmission technologies into clear, valuable insights that help our customers stay ahead in a fast-evolving digital world.
By turning complex technical concepts into practical, business-driven content, I aim to empower decision-makers with the knowledge they need to make confident, future-ready choices.
 Internet Data Center
Internet Data Center FAQs
FAQs Industry News
Industry News About Us
About Us Data Center Switch
Data Center Switch  Enterprise Switch
Enterprise Switch  Industrial Switch
Industrial Switch  Access Switch
Access Switch  Integrated Network
Integrated Network  Optical Module & Cable
Optical Module & Cable 








 Call us on:
Call us on:  Email Us:
Email Us:  2106B, #3D, Cloud Park Phase 1, Bantian, Longgang, Shenzhen, 518129, P.R.C.
2106B, #3D, Cloud Park Phase 1, Bantian, Longgang, Shenzhen, 518129, P.R.C.